Hey! Today i am going to explain javascript promises and promise chaining with the help of illustrations in this blog.
1. JavaScript Promise
- To manage asynchronous operations,we use Promise.
- It is used to determine whether or not the asynchronous operation was successful.
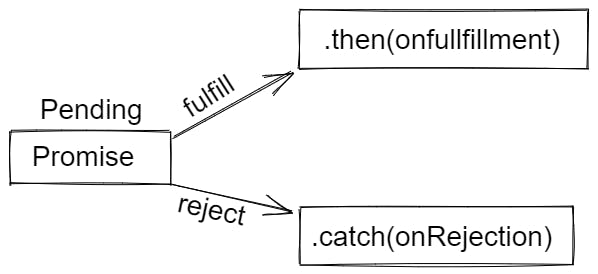
- Three states of promise are :-
- Pending
- Fulfilled
- Rejected
- A promise is made when it is still pending. That implies that the procedure is not finished.
- The operation concludes in a fulfilled state if it is successful.
- And, the process end in a rejected state,if a error is made.
2. Create a JavaScript Promise
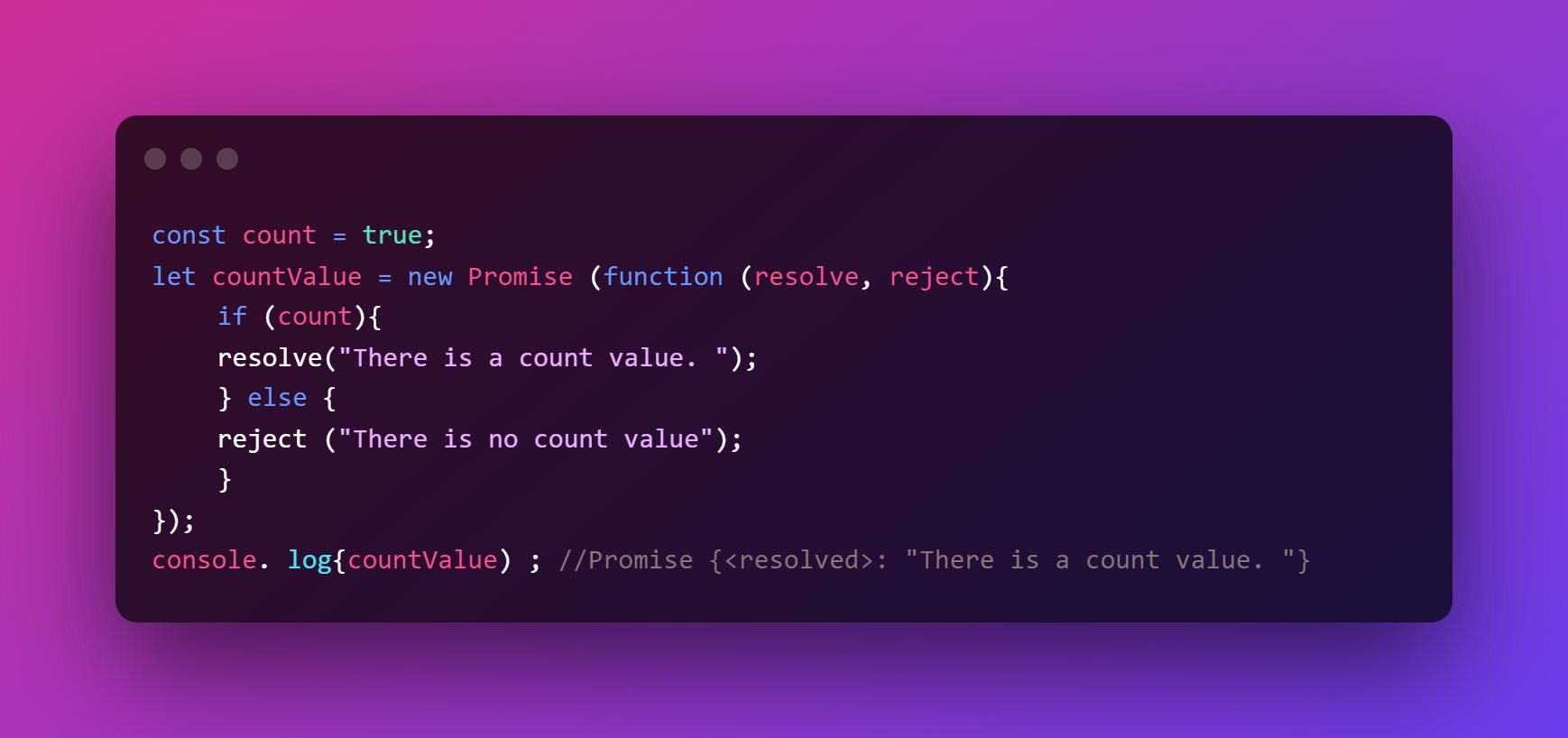
let promise = new Promise (function (resolve, reject){
//do something
});
We use Promise() constructor to create a promise object.
The resolve() method is called if the promise is successfully fulfilled.
The reject() method is called if there is an error.
- Here is an example of an asynchronous program and a promise can be used to manage the program.
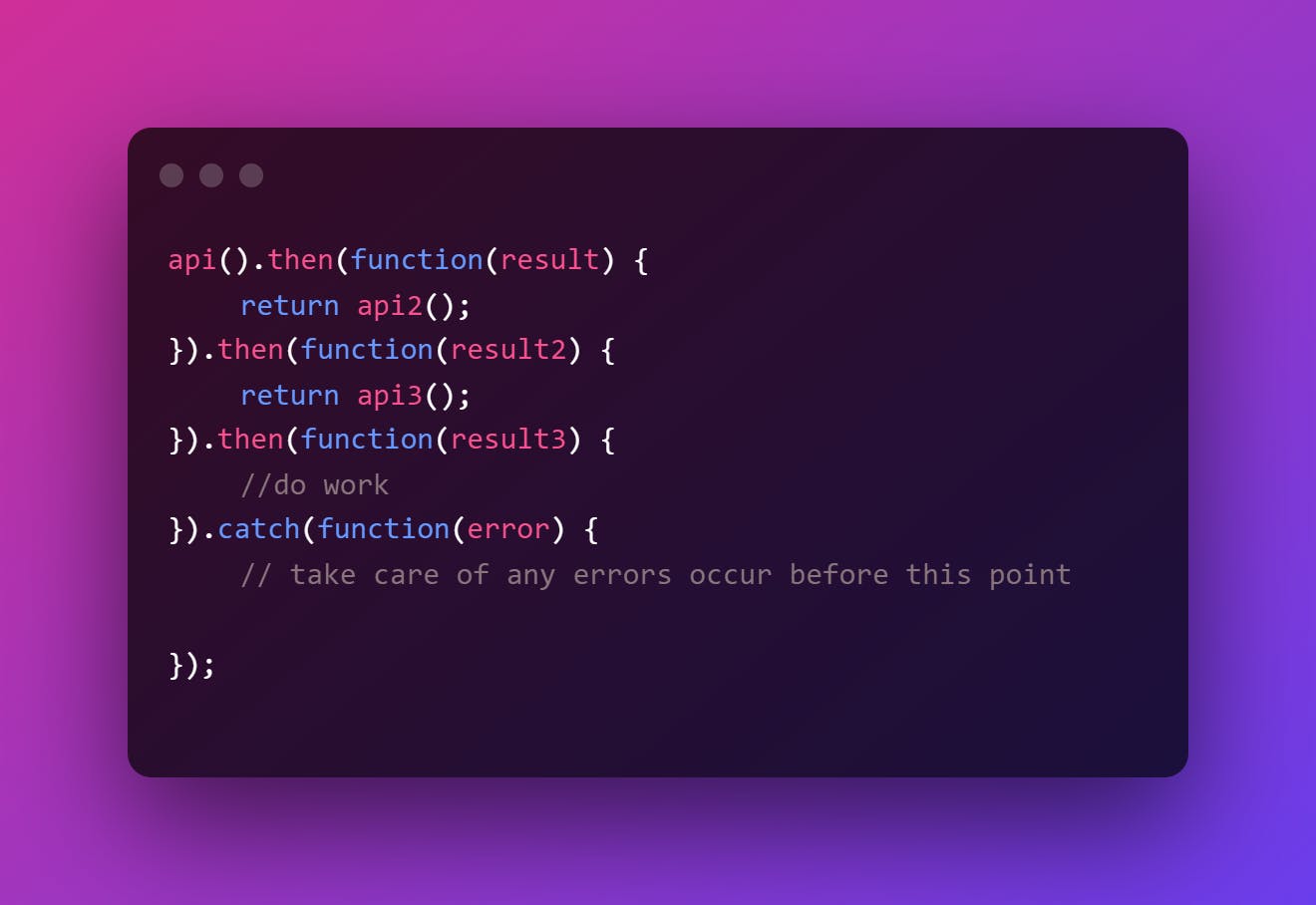
3. Promises chaining
When you need to manage multiple asynchronous tasks sequentially, promises come in handy.
We use promise chaining for this.
Using the methods like then( ) and catch( ) you can carry out an action once a promise is fulfilled ( ).
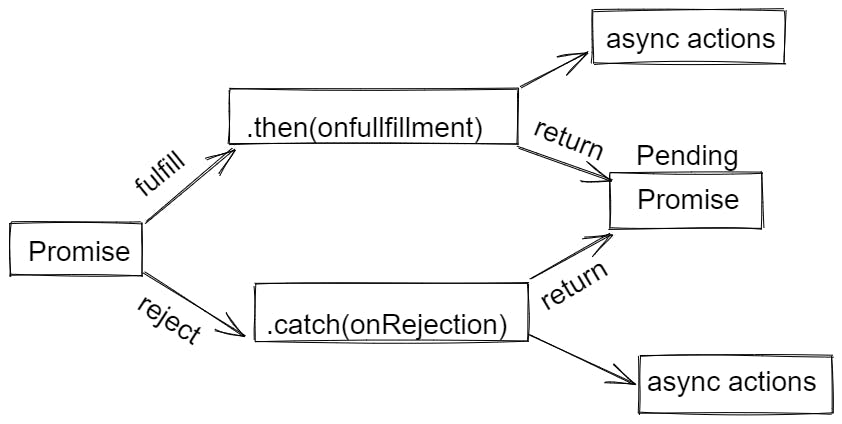
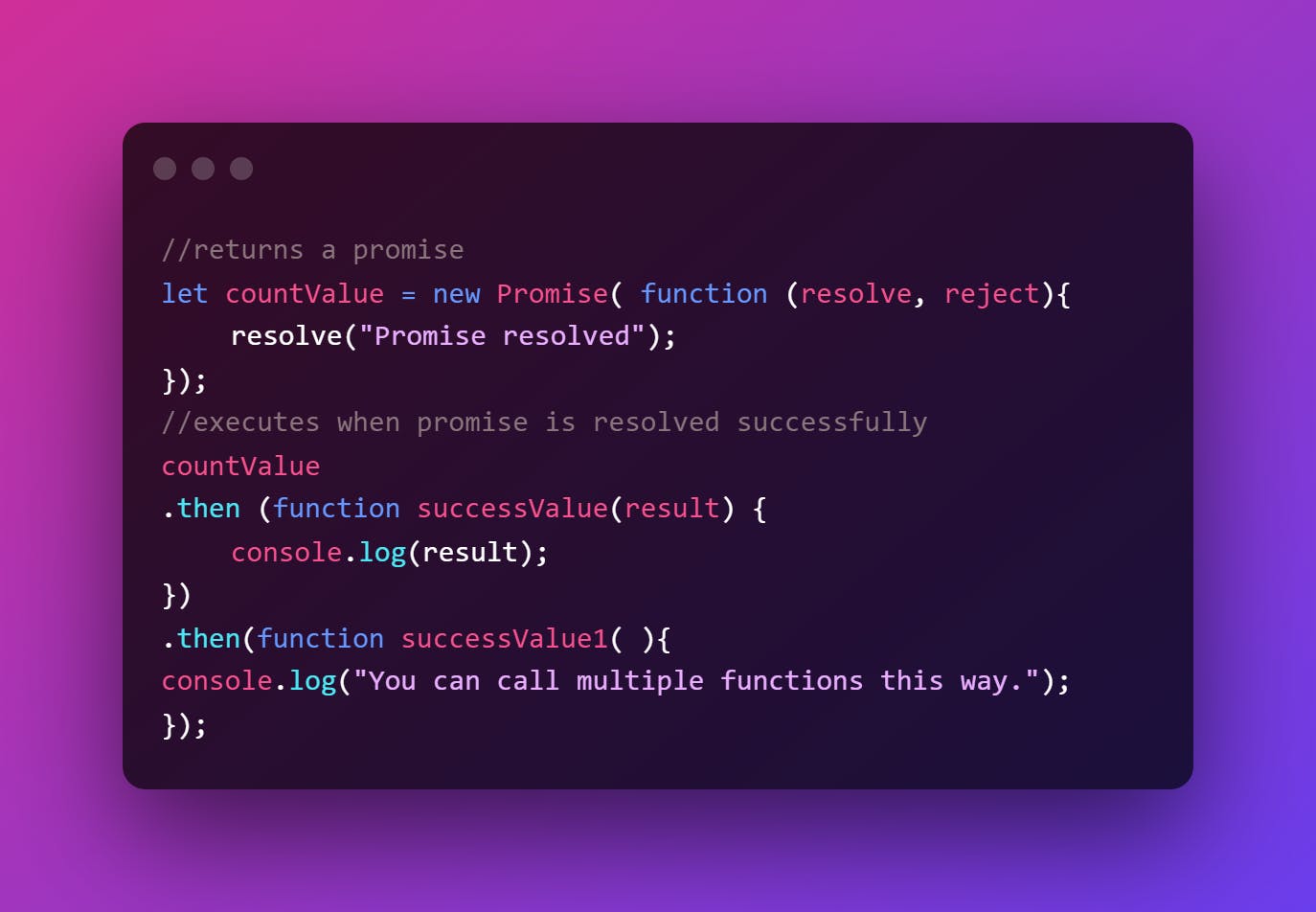
4. then( ) method
When the promise is properly fulfilled or resolved, the then( ) method is used with the callback.
The promise allows you to use a chain of multiple then( ) methods.
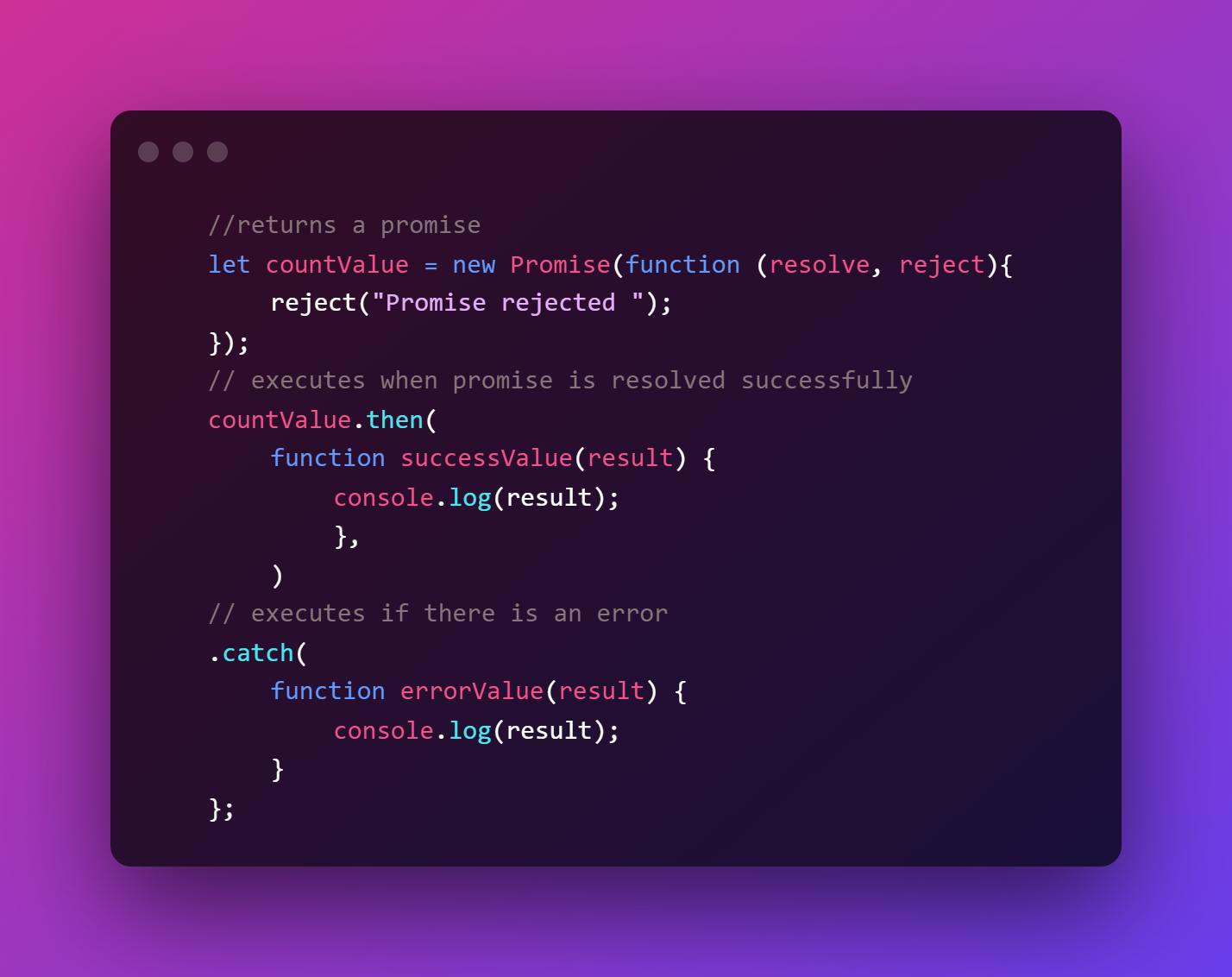
5. catch( ) method
- When the promise is declined or if an error occurs, the catch( ) function is used with the callback.
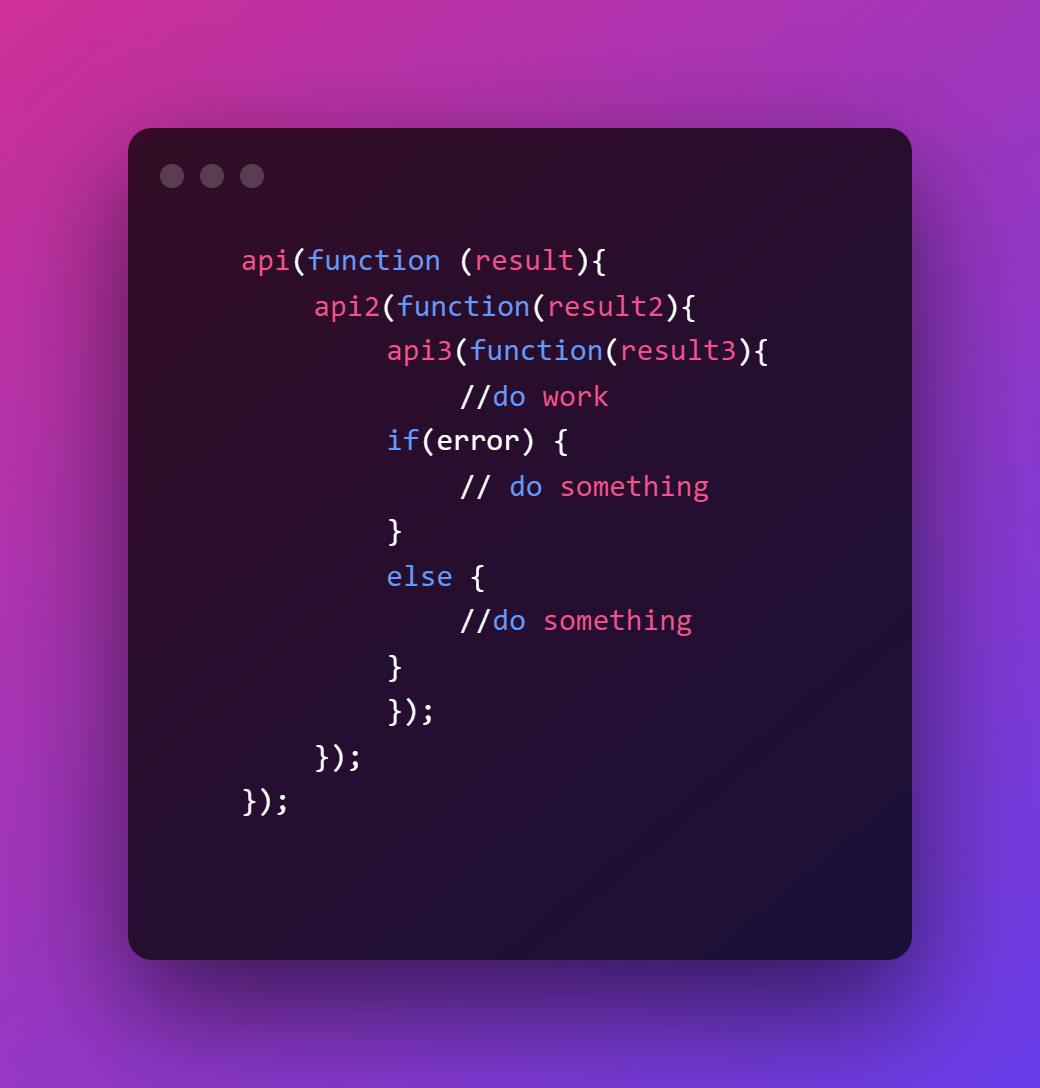
6. Promise vs Callback
Javascript Promise
The syntax is simple to read and understand.
It is simpler to handle errors.
Javascript Callback
- It's challenging to comprehend the syntax.
- It could be challenging to manage error management.